Injection Plastic Mold
Plastic Mold Manufacturer

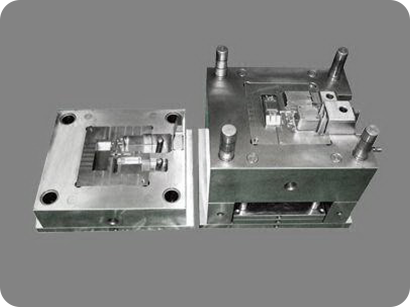
What Is A Plastic Injection Mold?
An injection mold forms molten plastic into a specific shape for various uses. The mold is designed by an engineer or industrial designer then the specifications are given to a tool or mold maker to implement. Plastic injection molds are typically made from steel, or aluminum precision machined to conform to the exact product design specification. Injected molding can be used to create a wide variety of product sizes and applications from an automobile body to small components used in a vast number of industries.
Advantages Of Injection Molding
01
Fast production and highly efficient. Injection molding can produce an incredible number of parts per hour. Speed depends on the complexity and size of the mold, anywhere between 15-120 seconds per cycle time
02
The low labor costs. Plastic injection molding is an automated process whereby a majority of the process is performed by machines and robotics, which a sole operator can control and manage. Automation helps to reduce manufacturing costs, as the overheads are significantly reduced.
03
Design flexibility. The molds themselves are subjected to extremely high pressure. As a result, the plastic within the molds is pressed harder and allows for a large amount of detail to be imprinted onto the part and for complex or intricate shapes to be manufactured
04
High-output production. Thousands of parts can be produced before the tooling needs to be maintained.
05
Large material choice. There is a large selection of polymer resins to choose from. Multiple plastic materials can also be used simultaneously; for example, TPE can be over-molded onto PP parts.
06
Low scrap rates. Injection molding produces very little post-production scrap relative to traditional manufacturing processes. Any waste plastic typically comes from the sprue and runners. Any unused or waste plastic, however, can be reground and recycled for future use.
07
Ability to include inserts. Metal or plastic inserts can be inserted molded
08
Good color control. Plastic parts can be manufactured in any required colors with the use of masterbatches or compounding.
09
Product consistency. Injection Molding is a repeatable process; in other words, the second part you produce is going to be identical to the first one, etc. This is a huge advantage when trying to produce high tolerances and part reliability in high volumes.
10
Reduced finishing requirements. There is often very little post-production work required as parts usually have a good finished look upon ejection.
11
Enhanced Strength. When plastic injection molding, it is possible to use fillers in the molding material. These fillers reduce the density of the plastic whilst it is being molded and can help add greater strength to the completed part
Disadvantages of injection molding
- High tooling costs and long setup lead times. Up-front costs are high due to the design, testing, and tooling required. There is the initial design and prototyping (probably via CNC or 3D printing), then the design of a prototype mold tool to produce replicas of the part in volume. Lastly, and only after extensive testing during both stages, you can finally inject mold apart.
- Part design restrictions. Plastic parts must be designed with injection molding consideration and must follow the basic rules of injection molding, for example
- Avoid undercuts and sharp edges as much as possible
- Use uniform wall thicknesses to prevent inconsistencies in the cooling process resulting in defects like sink marks.
- Draft angles are encouraged for better de-molding.
Don’t forget, because tools are typically made from steel or aluminum, it can be difficult to make design changes. If you need to add plastic to the part, you can make the tool cavity larger by cutting away steel or aluminum. But in order to take away plastic, you need to decrease the size of the tool cavity by adding aluminum or metal to it. This is extremely difficult and in many cases might mean scrapping the tool (or part of it) and starting over.
Also, the weight and size of the part will determine the tool size and necessary press size. The larger the part, the more difficult and expensive it will be.
- Small runs of parts can be costly. Due to the complexity of tooling, and the necessity to rid the machine of all previous material before the next product can be made, the setup time can be quite lengthy. Therefore small runs of parts have traditionally always been thought of as too expensive to injection mold.
How Are Plastic Molds Made?
Tooling that is made for plastic injection molding companies to manufacture custom plastic parts is
manufactured in multiple steps or stages.
manufactured in multiple steps or stages.
Manufacturability And Feasibility
The first step requires manufacturing specialists to collaborate and establish the product specifications, appropriate materials, and component functionality. The team of engineers and production technicians identify any potential design constraints, geometries that could introduce technical issues, or features that require special tooling requirements such as slides, lifters, or threading. They determine the desired plastic material for the product before selecting the optimal metal for the mold to ensure it facilitates the physical, chemical, and cooling properties of the injection molding material. Several tests are done, including mold flow evaluation, a manufacturability review, and a PFMEA or process failure mode effects analysis
Preliminary Design
The preliminary design stage uses models to determine the ideal mold and steel concept for the product. The design is marked up with changes to be finalized after review and approval.
Final Design Specifications
At this stage of plastic injection molding manufacturing, the mold builder gets the final design specifications. The mold maker can then implement any final adjustments or modifications to ensure it conforms to dimensional and manufacturability requirements.
Construction Of The Injection Mold Tooling
At the start of the mold construction the team has completed the tool drawings and reviewed the manufacturing standards. The plastic mold manufacturer creates a detailed plan for ordering the proper components and employs highly skilled mold making staff and precision machinery to create every detail of the new plastic injection mold. The mold construction timeline can range from 5 days to 16 weeks depending on the complexity of the product and mold design
In-House Initial Samples
Before the initial samples are created, the team establishes a molding process that the manufacturing department approves. The manufacturing process will go through a rigorous series of trials to find the optimal temperatures, times, pressures and speeds for the final approved injection molding process. The sampling process can take several hours or days depending on the dimensional or appearance requirements of the final product.
Make Any Final Tool Corrections
The final step in the plastic injection molding manufacturing process involves verifying the mold construction did not have any trouble producing parts to the product specifications and documenting the detailed procedure for future use. The parts that conform to the customer specifications are then submitted to the customer. Once the customer approves the sample, the full production process can commence.
Common Types Of Plastic Used For Molded Parts
Choosing the right material for your injection molded products is one of the most critical aspects of product development and injection mold design. It not only determines a lot of the molding cost, but also the part performance. Many material choices are available depending upon the application that impacts the part’s strength, flexibility, durability, color, and cost. Some of the most common include:

Nylon (Polyamide)
Nylon is often used for mechanical parts requiring strength, toughness, high melting points, as well as good chemical and wear resistance. Examples include automotive components such as bearings, bushings, gears, and quick-release buckles.
Acrylic
Acrylic is used in applications that require transparent parts. Because of its excellent clarity and weight advantage, it is ideal as a glass alternative.
Polycarbonate
This durable thermoplastic is approximately 200 times tougher than glass and has excellent clarity.. It is used as a much stronger alternative to acrylic.
Polyoxymethylene (POM)
POM is a strong, tough, and rigid acetal material that serves as an alternative to metal in some cases where high resistance to solvents is required, such as automotive parts like gears and bearings.
Polystyrene (PS)
There are two commonly used types of PS: High Impact Polystyrene (HIPS) and General Purpose Polystyrene (GPPS). GPPS is transparent, and HIPS is opaque. They are inexpensive and sturdy enough for toolboxes and power tools.
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)
ABS is an opaque engineering-grade thermoplastic that is very tough with impact, scratch, break, and tear resistance. Because of its low melting point and price, it is often used for keyboards, phone adapters, and wall socket guards
Polypropylene (PP)
Polypropylene is a thermoplastic most commonly used for food storage and packaging due to its ability to prevent chemicals from contaminating food. It does not degrade in hot water and has high elasticity, toughness, moisture, impact, and chemical resistance.
Polyethylene (PE)
This lightweight thermoplastic is water-resistant with high elasticity and chemical resistance, as well as electrical insulating properties. It is used for various products, such as fuel tanks, children’s toys, and trash cans.
Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU)
TPU has excellent elasticity, high tensile and tear strength, and withstands a wide range of temperatures, making it ideal for power tools, sporting goods, cable insulation, and seals.
Thermoplastic Rubber (TPR)
TPR is a recyclable mixture of rubber and plastic with high impact strength and superior chemical and weather resistance. It is often used for headphone cables, medical catheters, and suspension bushings. Calculating the Cost of a Plastic Injection Mold.
When it comes to injection molding cost, several factors can influence the cost of a plastic injection mold, including:
- Mold construction
- Number of mold cavities
- Part complexity
- Part size
- Plastic Material choice
Low volume vs.high volume production runs, what need to consider?
Within the injection molding industry there are several niche groups of manufacturers. A low-volume injection molding manufacturer is normally a fast and low-cost way to produce part orders less than 100,000 parts per year. A mid-volume plastic molded parts manufacturer routinely produces runs of 100,000-1,000,000 components. For orders above 1,000,000, high-volume injection molding manufacturers are best equipped.
